Quality planning best practice for medical device and GMP
- Kazi
- Last modified: August 17, 2024
What is quality planning?
Quality planning in GMP involves meticulous planning, process design, monitoring, and improvement of key business processes to meet legal, regulatory, and customer requirements.
Like pharmaceuticals, medical devices are manufactured, tested, and released to customers following stringent quality management systems. There are regulatory requirements to comply with, and the voice of the customer must be met.
Quality planning is the blueprint to generate ultimate customer confidence and satisfaction with the products you manufacture.
This article provides an in-depth look at how you, as a professional in a GMP business, can prepare quality planning documentation, especially from the perspective of a medical device manufacturing business. Your role is crucial in ensuring all necessary steps are taken to achieve compliance and business success.
The article aims to identify the processes and document the steps involved in planning total quality management in a medical device manufacturer and distributor.
Effective quality planning ensures compliance with legal, regulatory, quality standards, and customer requirements while achieving planned business objectives.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
Fundamentals of quality planning process in GMP
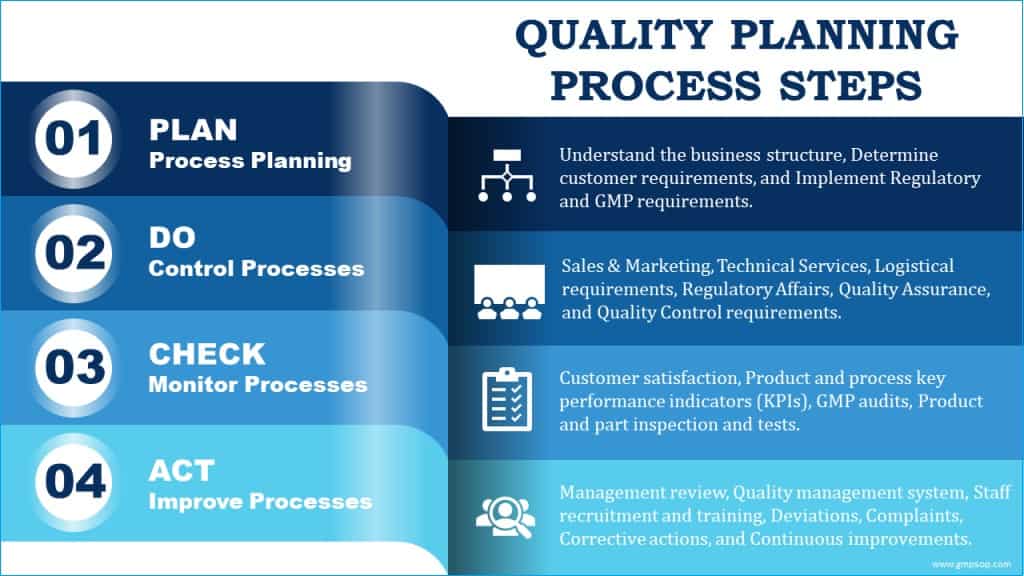
It is easier to understand the quality planning process by splitting it into four fundamental building blocks or elements: plan, do, check, and act.
1. Plan: planning processes
i. Understand the business structure
a. Set business objectives
b. Plan business resources
ii. Customer service requirements
a. Determining customer requirements
b. Sales & marketing processes
c. Customer service processes
iii. Implementing GMP requirements
a. Meeting legal and regulatory requirements
c. Business continuity planning
2. Do: processing controls
i. Sales & Marketing
ii. Technical services requirements
a. Calibration & maintenance
b. Service & Repair
iii. Logistical requirements
a. Storage & despatch
b. Purchasing
iv. Regulatory affairs & QA processes
a. Documentation control
b. Product Registration
c. Control of nonconforming material
3. Check: monitoring processes
i. Customer satisfaction
ii. Product and process KPIs
iii. GMP audits
iv. Product & part inspection and test
4. Act: improvement of processes
i. Management review
ii. Quality management system
a. Staff recruitment and training
b. Product complaint and corrective action
c. Customer service complaints
d. Continuous quality improvement
e. Quality records
This article only serves the vital areas of quality planning activities. It does not provide details of every possible business function that needs to be included in the quality planning.
Each manufacturing business should establish detailed standard operating procedures, manuals, and instructions relevant to the business functions, ensuring adherence to gmp standards.
This collection of documents should comprehensively demonstrate the mechanisms, controls, and responsibilities of identified activities.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
Quality planning process best practices (Plan)
A medical device processing business must apply the following control mechanisms in its processing areas to ensure that planning for quality is successful.
The business should recognize that quality planning is essential to achieving efficiency of the quality management system and the safety, quality, and reliability of the products supplied.
Efficient quality planning will meet the customers’ requirements and pave the way for the business’s ongoing success and growth, a journey to GMP compliance all staff will be part of.
Incorporate your quality management system documentation, such as quality manuals and all referenced procedures and records representing the business’s operations, into quality planning.
These are supplemented by working documents such as generic or product-specific work instructions, inspection and test methodologies, forms, registers, etc.
The quality procedures for a medical device facility include quality policies and manuals. All referenced procedures and records representing the business’s operations documents must reflect the requirements of the ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 standards and the adopted methods and processes by which the business’s mission statement, principles, and objectives are to be addressed and maintained.
Quality planning for a pharmaceutical processing plant must be based on GMP guidelines provided by regulatory bodies, such as the FDA guidance (Food and Drug Administration), EMA guidelines (European Medicines Agency), and WHO (World Health Organization) guidelines for pharmaceuticals.
Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is mandated for the success of quality planning.
i. Understand your business structure
It would be best to comprehensively describe your understanding of the business structure during quality planning.
For example, the business structure of the medical device site must be designed and developed to ensure that the quality management system is built in accordance with the requirements of ISO 9001 quality management and ISO 13485 – medical devices management system.
Develop quality policies and objectives to fulfill customers’ requirements effectively.
Define specific responsibilities and levels of authority for all individuals within the business structure, including reporting, communication lines, and the interrelationship of activities.
When preparing the structure, please make sure the business knows the importance of planning for its objectives and continual improvement of its business and services.
Accurate identification and establishment of control mechanisms within the business structure is vital to support the subsequent activities within the quality assurance and quality control functions.
a. Set business objectives
Clear and precise business objectives in quality planning ensure long-term business success.
During planning, you must ensure that all stakeholders recognize, agree on, and are committed to implementing corporate and quality objectives to guarantee optimum success.
Communicate your business objectives throughout the organization so that the departmental and individual staff members’ goals can be aligned to support overall business objectives.
Once you measure how promptly and effectively these objectives are implemented, you can get a fair idea of how to develop future goals and improvement plans.
b. Plan business resources
Determine the necessary level of skills and competencies for each position within the business structure to maintain the effectiveness of the quality management system.
Carefully recruit personnel and assign tasks, considering the required education, skills, experience, and knowledge, to ensure the desired level of competency for each position is achieved.
Maintain ongoing competency and suitability assessments to identify additional training needed to supplement productivity.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
ii. Customer service requirements
Describe all your customer service processes and requirements in the quality planning process. The objective is to develop a precise mechanism to satisfy customer needs.
Where possible, analyze customer feedback and utilize that to improve your current process and future quality improvements.
a. Determine customer requirements
Assessing and understanding the customer’s requirements is critical to achieving customer satisfaction. Information on customer requirements is collected through questionnaire surveys, workshops, market analysis, and direct meetings.
b. Streamline sales & marketing processes
Apply specific mechanisms to ensure that customer, product, and quality requirements are fully assessed and documented before providing a quotation for a contract.
Be sure to present accurate information in the product brochure, sales advertisement, and tender response to comply fully with legal and ethical requirements.
Develop suitable training programs for sales and marketing staff to consistently uphold the ethical standards that align with the business objectives.
c. Customer service processes
Comprehensive process maps must exist for the processes undertaken by the customer service department to ensure that the customer’s requirements are understood and acted upon promptly.
Please ensure the customer service department regularly interfaces with all other departments and that the activities are included in the department’s relevant process maps.
Design mechanisms to check the information upon receipt of a customer order and confirm that the customer’s requirements will be met.
Customers are contacted when their specific requirements, such as product type, quantity, and delivery timeframe, cannot be met. The issues should be discussed, and both parties agree upon a course of action.
The team should contact the customers whose order requirements are unclear or may contain information anomalies.
iii. Implementing GMP requirements
Medical device manufacturers and distributors must follow appropriate local and internal regulatory guidelines on good manufacturing practices while designing and developing products.
Please make sure you know all the regulatory requirements and controls you have implemented in your quality planning document.
a. Meeting legal and regulatory requirements
The business must be committed to meeting all its obligations relating to regulatory and legal requirements, whether concerning its ongoing operations or the safety and efficacy compliance of the products being distributed.
As part of setting new business objectives, including launching new products into the market or restructuring the quality management system, the business should thoroughly review all legal and regulatory requirements and ensure all activities are undertaken to ensure all company’s obligations are fully met.
b. Risk management
The ISO 13485 standard provides the basis for the business’s approach to quality risk management.
Based on my experience in risk management practice, the most prolific outcome from a risk assessment is achieved when the staff is adequately trained and enthusiastically participates in the brainstorming process.
In quality planning, the medical device business should promote a culture of risk-based decision-making when determining production process risks and consider control mechanisms. Mitigation approaches should be included while designing activities within each process.
You should ensure checkpoints are placed at strategic points in the business’s processes to prevent errors or anomalies from passing undetected down the process chain, which could negatively impact other internal or external stakeholders.
The quantity, location, and effectiveness of such process checkpoints are constantly reviewed for suitability, and checkpoints are moved, added, or removed to ensure the process runs at optimum efficiency.
c. Business continuity planning
The business should undertake an extensive review of the critical business processes and determine the minimum resources required to maintain them at a reduced level if a significant adverse event disrupts operations.
Each department must develop its business continuity plan, identifying the potential impacts, the resources required, the timeframe involved, and the specific activities to be undertaken in the event of an adverse incident.
You must ensure the departmental plans address all potential adverse events and contain relevant business continuity and recovery plans, which are essential to steering the business away from danger.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
Types of process controls required in quality planning (Do)
The activities in the planning phase we have explored so far typically drive the process control mechanisms.
Once the initial assessment and planning phases are undertaken, the processing activities take over, and the services are activated.
Ensuring that the product or service meets the customer’s requirements is part of these activities.
i. Sales & marketing process controls
The business meets face-to-face with the customer in the sales and marketing process. Please ensure these processes have been planned to identify and act on the customer’s requirements as a priority concern.
After securing the sale of products, ensure the sales and marketing procedures are designed to provide an accurate means of reporting sales figures back to the business.
This information is critical in assessing how well the business’s sales are progressing compared to the budget.
ii. Technical Services requirements
The technical service team plays a critical role in controlling manufacturing processes. Describe your validation master plan, instrument calibration, and maintenance schedule in the quality planning.
Present the technical service activities, process flow, and internal relationships in flow diagrams and decision trees.
a. Calibration and maintenance
The acquisition and control of tools, jigs, and test and inspection equipment are strictly controlled to ensure that equipment suitability, functionality, and stability result in fully conforming products provided to customers after repair and servicing.
During the initial planning of the repair and service processes, identifying the appropriate equipment, including the requirement for periodic maintenance or calibration activities, is assessed and documented.
b. Service and repair
In quality planning, ensure equipment service and repair activities are planned with the original manufacturer. Recognize that you, as the medical device manufacturer, remain the design authority for the device.
The business should ensure that it has ready access to the latest versions of the work instructions, test instructions, and operator manuals for all equipment being serviced or repaired.
Where applicable, test equipment and software programs will be validated before use in accordance with the manufacturer’s validation protocols and periodically reviewed for desired performance.
Please make sure that appropriate protection mechanisms are identified and utilized when a specific environment is necessary, such as taking precautions against electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage to components.
The medical device business should have a plan to electronically control product forecasting, ordering, receipt, dispatch, and financial accounting processes.
The business’s IT systems should share the same security and backup features and have local disaster recovery procedures in place to allow system recovery in the shortest possible time in case of a major system crash.
iii. Logistical requirements for medical device
Business success heavily relies on the efficiency and performance of the logistical arrangements. In the quality planning, you should include a logistical process map and a comprehensive mechanism to control the requirements.
a. Storage and despatch
The handling, storage, and despatch of goods must be carefully controlled, ensuring that full product traceability is maintained to customers before and after despatch.
Handling and storage conditions should be employed, which provide the optimum protection and preservation of the products and ensure that any sterilization is not compromised.
If applicable, specific requirements, such as environmental control, are identified during the planning stages, and the appropriate mechanisms are introduced to provide the correct storage conditions.
b. Purchasing
The purchasing process should include controls for evaluating and selecting suppliers, identifying and communicating product requirements, and verifying the procured material.
The above activities must be tightly controlled to meet the customer’s needs.
A structured supplier performance monitoring system provides data to indicate where improvement actions may be required.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
iv. Regulatory affairs, quality assurance, and quality control
Regulatory affairs, quality assurance, and quality control functions are integral to quality planning.
Your plan should include all quality assurance activities, such as manufacturing process operating instructions, product specification, testing methods, change management, deviation investigation, complaint handling, corrective and preventative action, etc.
a. Document Control
The correct identification, availability, and content of documents within the medical device business is vital.
Quality documentation incorporates departmental policies, manuals, SOPs, operator instructions, forms, logs, etc.
You should develop systems to assess new document requirements and amend the documents where a change is initiated. Document change control mechanisms will ensure the generation, approval, and distribution of new and amended documents.
The system should ensure that only current documents are available, with obsolete documents removed at the point of use.
Also, the business should have procedures for retaining and retrieving superseded documents and all quality records.
b. Product Registration
Establish communication channels with regulatory affairs at each affiliate manufacturing business. This will ensure that when new product registrations are submitted to the regulatory authorities, the manufacturer promptly and accurately supplies all the required information.
The Regulatory affairs and quality assurance staff should attend regulatory seminars where necessary to ensure they are conversant with all the current and proposed changes to the local regulatory requirements.
c. Control of non-conforming material
Where products, materials, or processes are found to deviate from planned or documented criteria, ensure their identification is quick and segregation controls are applied.
At the point of the deviation being reported, a risk assessment on severity and likelihood will be conducted, and the deviation will be classified as minor, major, or critical.
Conduct a root cause analysis using appropriate tools, such as cause-and-effect analysis, to correctly identify the incident’s root cause. Prepare corrective and preventative actions (CAPA) to prevent future recurrence.
The actions and responsibilities involved are documented to prevent the unintended use or delivery of nonconforming material.
How do you monitor processes in quality planning? (Check)
The availability of efficient monitoring and measurement mechanisms is critical to meet the business’s quality objectives. The following are the key monitoring activities that should be part of your quality planning.
i. Customer satisfaction
The collection and analysis of information relating to customer satisfaction is a key activity in improving the business.
Collect information and feedback actively through customer complaints, customer satisfaction questionnaires, and meetings between customers and medical representatives.
Analyze the customer data to identify areas for improvement and implement corrective and preventative actions. Review and measure the effectiveness of these actions periodically as part of the monitoring mechanisms.
ii. Product and process key performance indicators (KPIs)
In the quality planning process, key performance indicators should be included in mechanisms for measuring all departmental activities. Each area gives vital information about the level of business efficiency and the quality of customer service.
The data collected is periodically analyzed and forms a significant input for the management review activity.
iii. GMP audits
Internal quality and GMP audits monitor the ongoing suitability and effectiveness of the quality management system.
These audits are performed against a planned schedule, which considers every aspect of the quality management system and every departmental activity within the business.
The internal audit’s findings provide significant input into the management review activities. The audit’s observations show which processes are working and which require corrections.
Plan the audit schedule to reflect increased surveillance of problem areas. Implement corrective actions where there are gaps to ensure high-quality is achived.
iv. Product and part inspection and test
Ensure that all new capital equipment undergoes an abridged functional test as per the manufacturer’s instructions before dispatch and that the results are documented.
Products that have been repaired or serviced by the business receive a full functional test following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Where applicable, all equipment test results and readings are documented and included in the equipment’s service history records.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
Improvement processes in quality planning (Act)
It is beneficial for the business to proactively seek opportunities to improve the existing quality system, the quality of the products, and the skills and resources available.
Discuss these improvement initiatives in the management reviews.
i. Management review
Senior management should regularly assess the suitability and effectiveness of the quality management system and review the business’s progress against its objectives.
These reviews should analyze the results of the various performance monitoring mechanisms and identify improvement opportunities for products, processes, and the quality management system.
ii. Quality management system for GMP
You have to include mechanisms to ensure that improvement opportunities in quality management systems are identifiable and acted upon through internal audits.
a. Staff recruitment and training
Businesses should recognize that staff recruitment, training, qualification, awareness, and personal development are central to achieving business objectives, meeting customers’ requirements, and ensuring continual improvement of the staff skill base.
Develop specific recruitment criteria to secure staff with the appropriate skills, competency, and experience relative to their position.
The business should monitor staff competency and identify training needs and effectiveness by performing periodic performance appraisals.
Employ internal and external training programs for staff at all levels within the business. Generate training records and the level of competency achieved.
b. Product complaints and corrective actions
Develop a mechanism to capture customers’ dissatisfaction with a product via survey and customer complaints system.
Prepare trend analyses and, where required, investigate the root cause of the complaints. Implement corrective action and document its effectiveness.
c. Customer service complaints
When a customer is dissatisfied with the quality of service and they wish to return the product, these actions must be formally documented via the warehouse material handling process.
Describe how the business can identify and implement improvement opportunities based on information collated via the customer satisfaction surveys.
d. Continuous quality improvement
Structure the quality management system to facilitate the continual improvement of all the business activities.
The cycle of collecting the data, implementing the actions, and then measuring the results should be applied across all quality system processes undertaken by the business.
Please make sure the staff are trained to assess the activities critically and learn to apply continual improvement where possible.
e. Quality records
All documents generated from the quality planning activities are classified as quality records and must be stored and archived according to good documentation practice.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quality planning is essential for medical devices and other GMP businesses. It serves as the blueprint for building customer confidence and satisfaction. You can meet quality, regulatory, and safety standards by establishing robust processes, control, monitoring, and improvement practices.
Quality planning involves systematically planning, doing, checking, and acting on various activities that generate high-quality products.
You have to ensure that all quality aspects are meticulously planned and executed to achieve such success.
From setting business objectives, understanding customer needs, and meeting GMP requirements to implementing effective process controls and continuous improvement initiatives, each step plays a critical role in achieving the desired quality outcomes.
This comprehensive approach not only ensures regulatory compliance but also instills confidence in your business operations.
Effective quality planning safeguards compliance with ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 standards and ensures the organization is prepared to handle regulatory challenges.
It facilitates risk management and business continuity and enhances overall operational efficiency.
By promoting a quality and continuous improvement culture, medical device manufacturers can maintain high standards, drive business success, and achieve long-term growth.

Author: Kazi Hasan
Kazi is a seasoned pharmaceutical industry professional with over 20 years of experience specializing in production operations, quality management, and process validation.
Kazi has worked with several global pharmaceutical companies to streamline production processes, ensure product quality, and validate operations complying with international regulatory standards and best practices.
Kazi holds several pharmaceutical industry certifications including post-graduate degrees in Engineering Management and Business Administration.

You are in reality a just right webmaster. The site loading velocity is incredible. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. In addition, the contents are masterwork. You have performed a wonderful task on this topic.