Nine steps for creating a Master Validation Plan
- Published on: Feb 20, 2021
You might be wondering what is master validation plan (MVP) and how to develop and implement one for your GMP facility. This article can help you understand the principle of master validation plan and what is involved in creating one.
If you are in pharmaceutical business it is mandated by the regulatory authorities to develop, implment and periodically review a master validation plan for qualifying your equipments, processes, cleaning systems, buildings and facilities etc. It is a regulatory requirement for you to create one master validation plan and implement in your site. If you are to make your product safe, pure, effective and identifiable at all times for human or veterinary use, you definitely need to create an effective master validation plan.
What Should be the Scope of a Master Validation Plan?
Master Validation Plan is a strategic document which identifies the elements to be validated, the approach to be taken for validation of each element, the organizational responsibilities and the documentation to be produced in order to ensure full consideration is given to product quality aspects. The plan should show how separate validation activities are organized and inter-linked. Overall, it provides the details and relative timescales for the validation work to be performed.
All functions, departments and manufacturing sites within the parent GMP sites or its contractors operating under GMP and GLP regulations or guidelines must reflect in the MVP. The plan applies to all existing and new drug compounds. It covers the planning of validation activities related to the manufacturing and control of the registered stages of Drug Product or Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) for clinical use, validation or sale.
All manufacturing activities concerned with the following scenarios validation activities should be carried out in accordance with approved procedures:
1. The receipt and establishment of new Drug Products or API’s.
2. Major processing changes to existing Drug Products or API’s.
3. The construction of new manufacturing or related facilities.
4. Major alterations to existing manufacturing or related activities.
Where a project consists of a range of different validation activities then a Master Validation Plan should be prepared. Different major projects carried out in one facility may each have it’s own master validation plan. Activities should be planned and prepared by local management who should approve essential documentation prior to starting validation activities.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.

Who are Responsible for Master Validation Plan?
Each site should have in place SOPs for the preparation of validation documents that take account of this, or are equivalent to, this guideline. This documentation and the MVP should be approved by the Quality Assurance Function.
It is the responsibility of each site to appoint an individual responsible for validation, nominally the validation manager for a validation project.
The validation manager should be responsible for all validation activities including the preparation of a master validation plan. The validation manager, together with the site management staff, is responsible for ensuring SOPs are in place for the preparation of related validation documentation.
The master validation plan should be prepared, commented on and approved by the senior site persons as agreed locally or nominated by a Steering Committee. QA approval is required. The approval signatures on the plan would normally be those of the site or manufacturing unit management team.
master validation plans should be prepared and managed by members of the manufacturing site where the exercise is to be carried out and utilize personnel competent for the tasks assigned. Where consultants are used to prepare plans, their work should be subject to the same level of scrutiny and approval as in-house documentation.
In the case where third party contractors are used to manufacture an intermediate or API it is the responsibility of the Quality Assurance team of the lead site to ensure that the facilities, equipment and processes at the contractor are qualified / validated in line with site requirements.
An Example of Computer System Validation in GMP
We have analysed a list of validation activities involved during Computer System Validation in a seperate article. The post describes validation lifecycle phases, deliverables and primary elements of computer system validation.
When Does a Master Validation Plan Required?
A master validation plan is needed when significant changes are made to the facilities, the equipment and processes which may affect the quality of the product. A risk assessment approach should be used to determine the scope and extent of validation. The master validation plan should be available prior to starting any of the validation activities.
A new master validation plan should be prepared for projects involving major change to existing equipment. A MVP is not required for projects, which involve the installation or alteration of a single item of equipment – these should be documented on separate validation plans and reports.
The master validation plan should be available prior to starting any of the validation activities. For some sites, both a site MVP (for the site’s validation requirements) and project specific MVPs may exist. The site validation committee should provide co-ordination as appropriate.
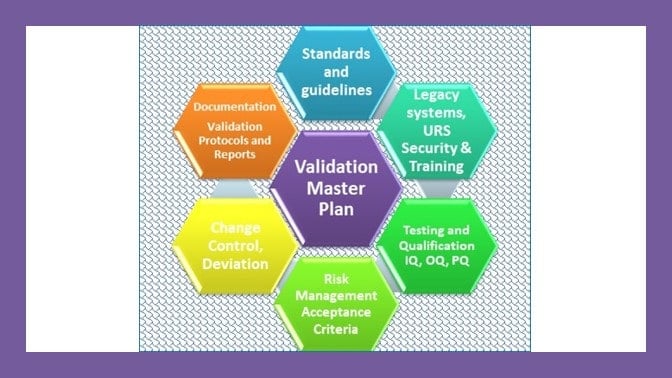
What Should a Master Validation Plan Contain?
Each master validation plan shall describe the scope of the activities and address relevant key elements of validation affected by the change, indicating the actions and documents that will be needed. The key elements are those factors that can have an effect on product quality.
The MVP shall identify all the components to be included within a validation project. Flow diagrams or matrixes can be useful to provide an overview and monitoring tool. A high level process map or flowchart of the manufacturing process should be included.
Following the issue of the master validation plan, detailed risk assessments (system and component impact assessments) should be carried out to identify items requiring qualification.
The content of the master validation plan should reflect the complexity of the extent of the validation activities to be undertaken. At minimum the MVP should address the following:
1. Title, statement of commitment and approval page.
2. Summary description of the project and its scope.
3. A statement of validation policy and the objectives of the validation activity
4. References to other existing validation documents.
5. A description of the organization and responsibilities for validation
6. The validation strategy to be adopted opposite Facilities and Systems(process equipment and services including automated systems), Materials, Quality Control, Personnel including training.
7. The intent in respect of Process Validation and Cleaning Validation for each of the drug product range.
8. The documentation management and control system to be used.
9. A description of the validation change management process.
10. An indicative relative timescale plan.
11. Clear acceptance criteria against which the outcome of the validation exercise will be judged.
The requirements for the above should be reflected in a completed Responsibility Chart for all deliverable documentation.
For large projects involving many materials, a Materials Validation Plan may be used. For smaller projects, a Materials Validation Plan is optional. The Plan or lower tier documentation alone may cover the qualification of materials.
The headings of the MVP may be based on the above list. A project may be organized in different ways, however, depending on the character of the project.
The validation plan should demonstrate that the validation activities have been considered and are being organized in a structured manner.
A master validation plan should be presented as a formal document which is suitable both as an internal guide and for scrutiny by a member of a regulatory inspectorate. It should therefore be concise, easy to read and not excessively duplicate text from documents held elsewhere in the Quality System.
Reporting Requirement for Master Validation Plan
Each validation plan should result in a report confirming that all validation activities have been completed satisfactorily.
It is recommended that a Summary Validation Report (or Master Validation Report) is prepared which summarizes activities undertaken, presents the overall conclusions and provides cross references to any associated reports or follow up actions.
Changes to Master Validation Plan
Master Validation Plan should be prepared and managed by members of the manufacturing site where the exercise is to be carried out and utilize personnel competent for the tasks assigned. Where consultants are used to prepare MVPs, their work should be subject to the same level of scrutiny and approval as in-house documentation.
Any changes from a master validation plan after issue, should be agreed with the steering committee for the project. The MVP should not be revised once the activities it describes have started. The changes should be recorded in the project documents derived from the MVP and be reported in the Master Validation Report.

Author: Kazi Hasan
Kazi is a seasoned pharmaceutical industry professional with over 20 years of experience specializing in production operations, quality management, and process validation.
Kazi has worked with several global pharmaceutical companies to streamline production processes, ensure product quality, and validate operations complying with international regulatory standards and best practices.
Kazi holds several pharmaceutical industry certifications including post-graduate degrees in Engineering Management and Business Administration.
Related Posts
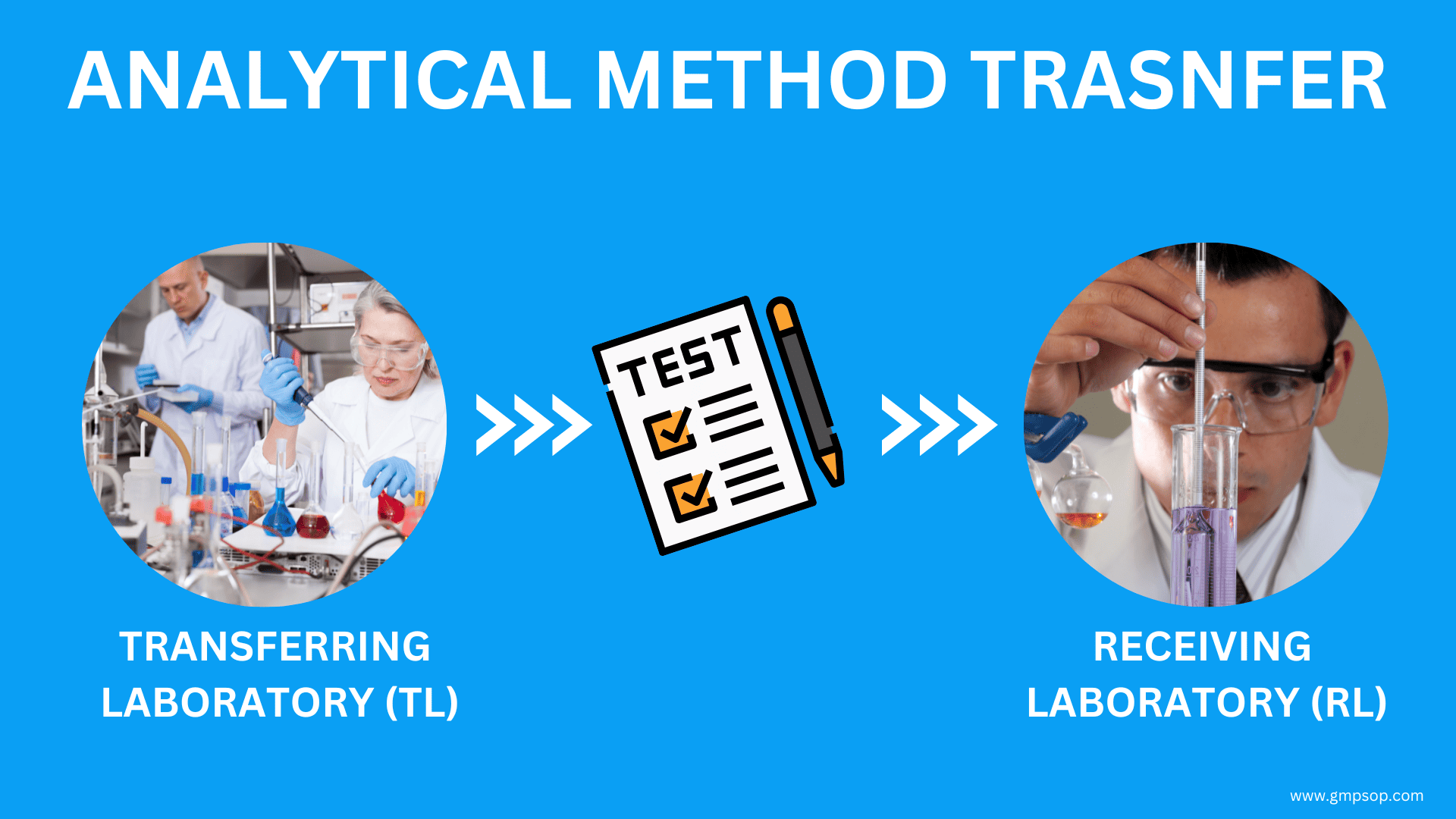
Importance of acceptance criteria in analytical method transfer
What is meant by reference standard in Pharmaceuticals?
Laboratory Waste Disposal Procedure at a GMP Site