How to conduct product quality review in pharmaceutical
- Published on: Nov 19, 2023
An annual product quality review is intended to provide information on a pharmaceutical product’s performance.
You should perform a product quality review annually to determine if any adjustments to product specifications, manufacturing process, or raw material supply are required to improve the product further.
The scope of this article applies to all regulated medicinal products manufactured at a GMP site that undergo annual product quality review.
The content of this article does not supersede or replace any local or international regulatory requirements. The content of this article should be considered as industry best practice in line with international regulations instead of mandated regulatory guidelines.
FDA Guidance for Industry Q10 for the pharmaceutical quality system has published detailed guidelines for conducting product quality reviews periodically.
When conducting an annual product quality review, your objective should be to verify the consistency of your manufacturing process.
To describe the procedure you must have a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP). Reporting templates should be available to ensure consistency in approach.
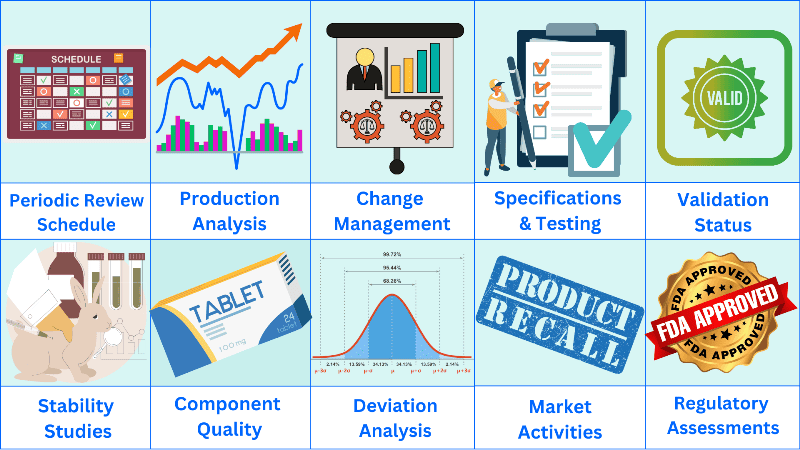
Product quality review schedule
The schedule should be completed on a yearly cycle. You may group the products into products with similar formulations and properties.
The schedule should include the following as a minimum:
– Product Review Period
– Product / API to be reviewed
– Product Review due dates
The product quality review report should be targeted for completion within three months of the end of the review period.
Product quality review content
First, could you set up an SOP that details the requirements of the product quality review? Templates should also be available to assist with the completion of the report.
After the product quality review, prepare a summary report with chapters covering all critical elements of the product life cycle.
At a minimum, the chapters should include:
– An analysis of the production process
– A review and investigation of all deviations and non-conformances
– A review of all approved change controls that could impact product quality, validation status, or regulatory filing for the product
– An analysis of the microbiological and chemical test results and conformance with specifications
– An analysis of stability studies and associated test results
– An assessment of component quality based on a review of the starting materials and primary packaging that comes into direct contact with the product
– A review of market activity, concentrating on product returns, complaints and recalls
– A regulatory assessment consisting of any changes to the specifications as registered by all relevant regulatory agencies
– An assessment of the validated or qualified status of all processing, cleaning, analytical methods, automated controls, or packaging validation
– An assessment of relevant suppliers and currency of relevant GMP agreements
Annual product quality review should make recommendations for improvement based on the analysis.
Just to let you know, confirmation of those recommendations should be adopted as required.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
How do you perform data analysis during quality review?
During the annual product quality review, data must be trended and analyzed to determine whether the process is in control and appropriate.
Control limits should be established and justified through trending. The trend will establish if current specifications for both starting materials and finished products are suitable.
Trending will help identify product and process improvements.
Graphical representation using control charts is used to identify trends.
If significant trends are identified, they should be documented, and changes should be made to avoid out-of-specification results.
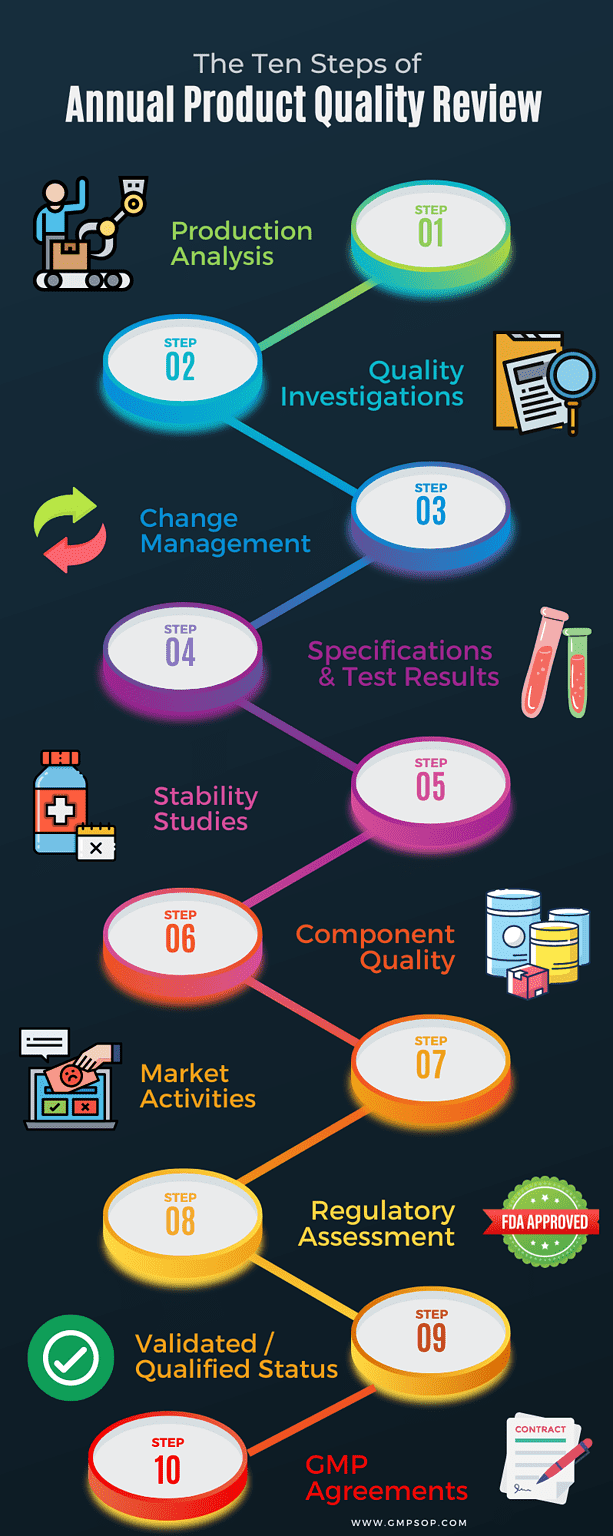
Level of details required in product quality review
a. Production analysis
The annual product quality review requires an assessment of the performance of critical processes.
Each batch must be reviewed to assess whether release parameters were successfully met and all critical processes were performed within set parameters.
All active ingredients and excipients will be identified.
The number of batches manufactured, released, and rejected should be documented.
All steps in the production process must be documented, and critical process parameters and quality attributes must be identified.
The batch records must be assessed to verify that all process steps are followed and checks are conducted.
b. Quality investigations
During the product quality review process, all deviations or non-conformances that may impact product performance must be reviewed.
The effectiveness of any corrective actions should be assessed.
Deviations should be itemized and, where possible, classified as Manufacturing, Laboratory, or Environmental.
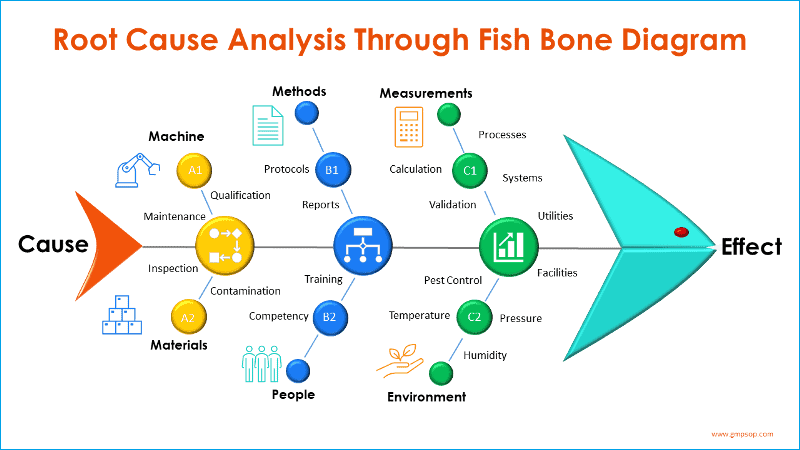
The root cause should be identified, and any corrective actions should be listed. You would need an assessment of the effectiveness of corrective actions.
Any significant deviations or trends should be analyzed and discussed.
c. Change management
All approved change controls that could impact product quality, validation status, and regulatory filing for the specific product must be reviewed.
A list of all changes made to the manufacturing process must be itemized with details on status, justification, and implementation date. Changes may include:
– Change in mixing or blending time
– Change in batch volume
– Change in filling speed
– Change in temperature for mixing
– Change in the vessel
– Change in inactivation or hold time
All changes to analytical methods must be assessed during the review. These may include:
– Change in solvents, buffers, or reagents
– Change in composition of mobile phase
– Change in HPLC method
– Change in incubation time or temperature
Any changes to product specifications should be documented.
Any changes that impact the product’s quality must be evaluated.
d. Specifications and test results
The analytical and microbiological release data for all batches manufactured during the product quality review period must be analyzed and charted to assess control and compliance.
Test results for each stage of the manufacturing should be tabulated and graphed.
Any trends should be analyzed. The root cause for any out-of-specification results should be provided.
e. Stability studies
Stability studies should be analyzed and trended to determine if there is any evidence of product deterioration over time.
All batches on stability test or have completed testing in the review period should be listed with details of the testing schedule, test conditions, and expiration date.
Trends or atypical degradation must be itemized and assessed against upper and lower specification limits.
Investigations of out-of-specification results must be included with the root cause identified.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.
f. Component quality
A review of all starting materials and primary packaging in contact with the product should be completed.
This will include supplier performance assessment and identifying any critical deviations associated with active or excipient ingredients, primary packaging, and closure material.
Suppliers of all active materials should be listed, and they should be considered as a suitable supplier.
I want to inform you that particular attention must be given to new suppliers.
All deviations associated with raw materials that may have product impact must be assessed concerning whether the material is an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), excipient, or primary packaging.
The impact of any raw material changes or deviations on the finished product must be assessed.
g. Market activities
A review of market activity should include all quality-related product returns, complaints, and recalls.
The product quality review will include details on investigations that occurred during identification.
You must have a summary of all complaints or adverse events during the review period. Details of how each issue was resolved should be provided.
Details of any recall activity must include the following:
– The reason for the recall
– Any investigations conducted
– Regulatory response
– Corrective actions
– Current status
Just to let you know, details of returned goods, quality issues, and final disposition of goods are required.
Any corrective actions that have been taken are to be assessed for efficacy.
h. Regulatory assessment
A summary of changes in specification registered with local or international government regulators must be included.
Any post-marketing commitments should be reviewed and their status assessed.
Any deviation notifications reported to regulatory agencies must be documented, and follow-up actions and current status must be identified.
Regulatory agency inspection commitments that relate specifically to the product must be outlined.
Any regulatory submission filed or closed during the review period is to be reported.
i. Validated / qualified status
The review should include details of all product-related validation activity initiated or completed during the product quality review period.
All validation/qualification studies commenced or completed during the review period must be assessed. These may include:
– Packaging validation
– Cleaning validation
– Analytical method validation
– Equipment validation
Any identified significant issues and deviations must be discussed and resolved, and the effectiveness of the validation must be determined.
j. GMP agreements
All GMP agreements relevant to the product or production process must be reviewed to ensure that the contract between manufacturer and supplier covers all aspects of manufacture.
All suppliers needing an agreement should be identified, and a reference should be provided to existing agreements.
Currency and relevance should be assessed concerning any revisions or changes.
GMP agreements should cover all technical requirements for periodic production and laboratory equipment maintenance.
Prepare a report on product quality review
The annual product quality review summary report should provide a comprehensive overview of the data contained within the different elements of the product review.
The summary needs to provide:
– An analysis of the performance of the products
– A review of all the elements reported
– A summary of any trends or concerns
– Identification of any previous issues or corrective actions
– A conclusion as to the suitability of the product for ongoing production
– A rating of product performance based on the report
The summary should stand alone as a report and provide sufficient detail for senior management to assess product performance.
Tracking the recommendations
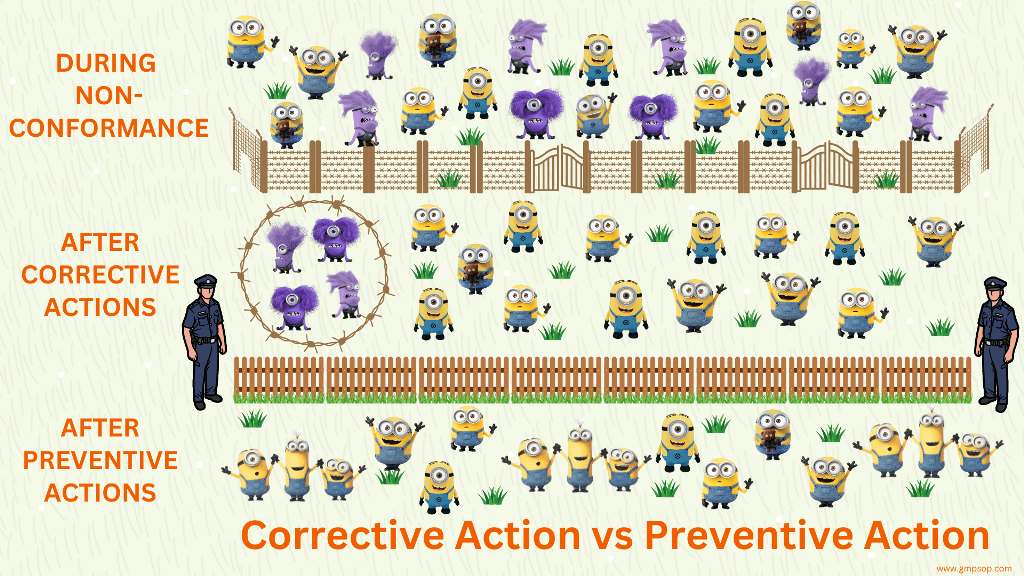
All annual product quality review recommendations must be addressed and tracked through the Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) program.
The CAPA should cross-reference the product quality review. Subsequently, the effectiveness of the corrective actions should be documented.
Approval and review process
The completed product review must be approved by the:
– Production Manager
– Quality Manager
Following approval, the controlled copies are to be circulated to the following:
– Production Manager Biologicals or Pharmaceutical (as relevant)
– Quality Control Manager
– Quality Assurance Manager
– Production Manager
The master document is to be maintained by the QA group.
Escalation of product quality review report
Any significant concerns about product quality or trends must be escalated to the head of the GMP site.
A list of substantial concerns may include the following:
– Consistently Out of Specification results
– Unexplained trends
– Regulatory commitments that have not been met
– Failed validations
– Regulatory non-compliance
– Anything that may result in product recall
Conclusion
The main objective of an annual product quality review is to see if your product consistently maintains its expected quality and to identify any needed improvements to ensure consistency with your manufacturing process.
You should have standard operating procedures and templates describing how to review individual aspects of product quality and how to trend your product quality.
The review analysis should cover areas such as production process, product specifications, major deviations, out-of-specification results, validation status, test methods and test results, stability studies, change of raw materials and packaging components, complaints, recalls, and other market and regulatory actions.
You must prepare a comprehensive summary report of your findings and observations from the review.
Use statistical analysis to prove if the product is maintaining its expected quality.
If you find any adverse trend during the review process, please take corrective and preventive actions.
Prepare your recommendations to improve the product quality in your summary report.
The conclusions drawn from the annual product quality review must be reviewed through the site quality council.
240 SOPs, 197 GMP Manuals, 64 Templates, 30 Training modules, 167 Forms. Additional documents included each month. All written and updated by GMP experts. Checkout sample previews. Access to exclusive content for an affordable fee.

Author: Kazi Hasan
Kazi is a seasoned pharmaceutical industry professional with over 20 years of experience specializing in production operations, quality management, and process validation.
Kazi has worked with several global pharmaceutical companies to streamline production processes, ensure product quality, and validate operations complying with international regulatory standards and best practices.
Kazi holds several pharmaceutical industry certifications including post-graduate degrees in Engineering Management and Business Administration.
Related Posts
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) Procedure for GMP
Best Microbiology Laboratory Techniques in Pharmaceuticals
How to conduct a root cause investigation using DMAIC principle